The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v1.13 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Dapr sidecar (daprd) overview
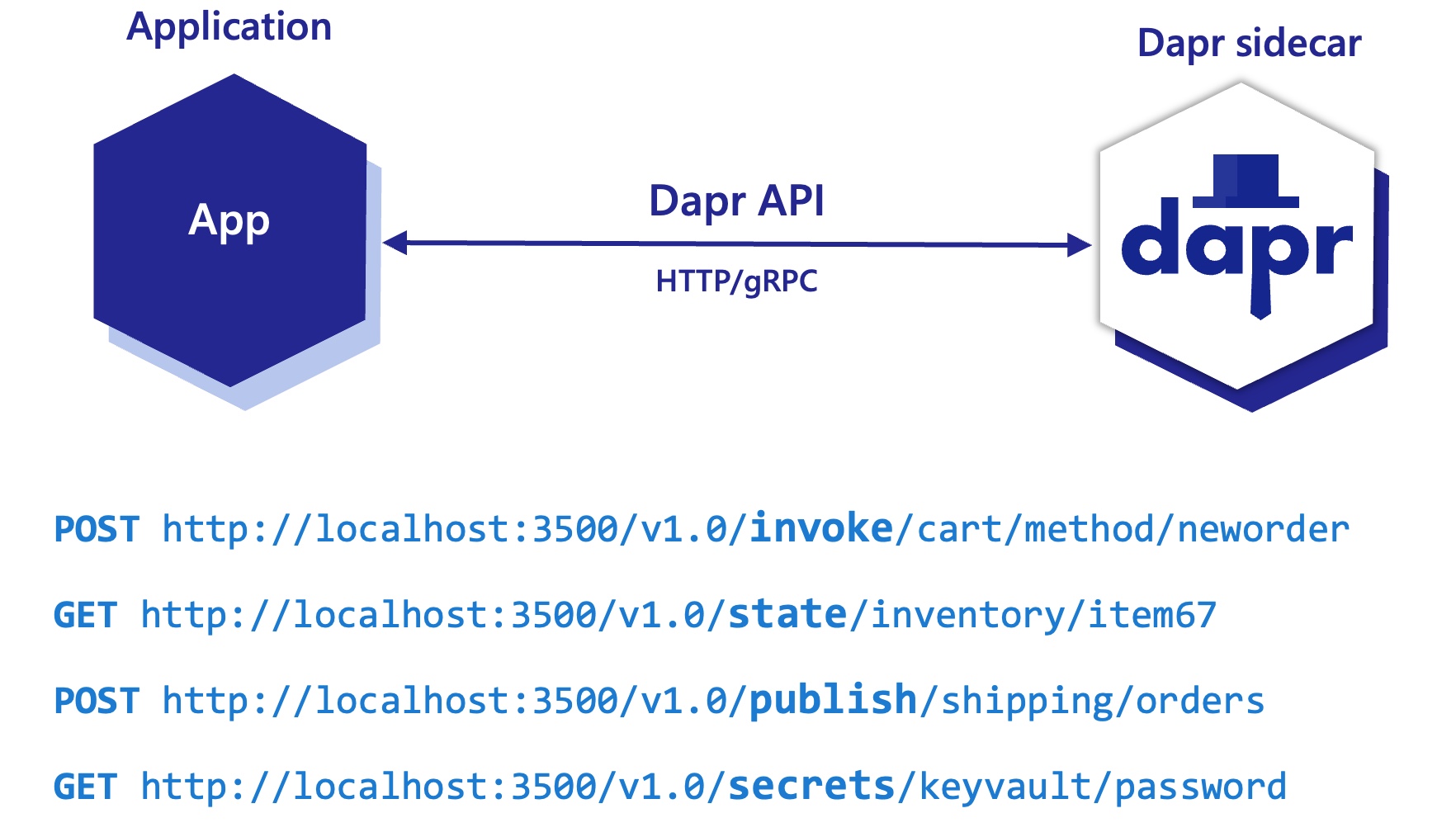
Dapr uses a sidecar pattern, meaning the Dapr APIs are run and exposed on a separate process, the Dapr sidecar, running alongside your application. The Dapr sidecar process is named daprd and is launched in different ways depending on the hosting environment.
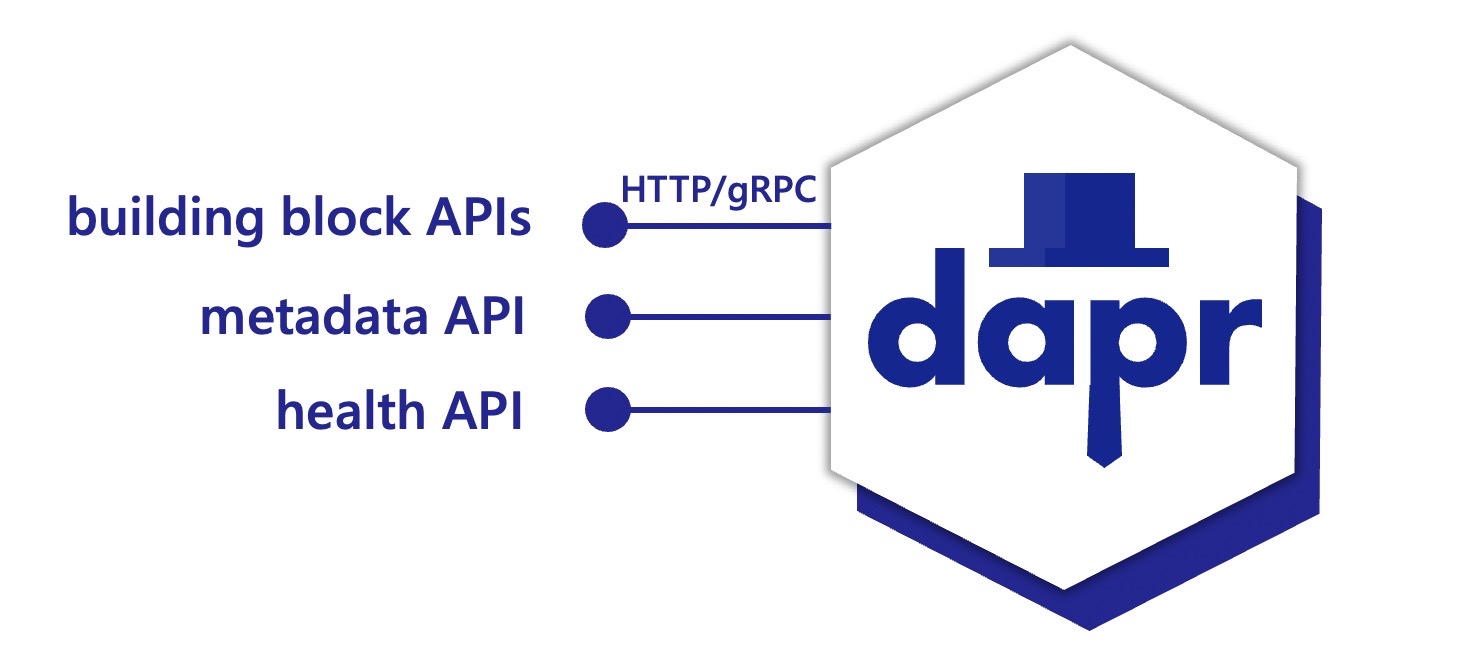
The Dapr sidecar exposes:
- Building block APIs used by your application business logic
- A metadata API for discoverability of capabilities and to set attributes
- A health API to determine health status and sidecar readiness and liveness
The Dapr sidecar will reach readiness state once the application is accessible on its configured port. The application cannot access the Dapr components during application start up/initialization.
The sidecar APIs are called from your application over local http or gRPC endpoints.
Self-hosted with dapr run
When Dapr is installed in self-hosted mode, the daprd binary is downloaded and placed under the user home directory ($HOME/.dapr/bin for Linux/macOS or %USERPROFILE%\.dapr\bin\ for Windows).
In self-hosted mode, running the Dapr CLI run command launches the daprd executable with the provided application executable. This is the recommended way of running the Dapr sidecar when working locally in scenarios such as development and testing.
You can find the various arguments that the CLI exposes to configure the sidecar in the Dapr run command reference.
Kubernetes with dapr-sidecar-injector
On Kubernetes, the Dapr control plane includes the dapr-sidecar-injector service, which watches for new pods with the dapr.io/enabled annotation and injects a container with the daprd process within the pod. In this case, sidecar arguments can be passed through annotations as outlined in the Kubernetes annotations column in this table.
Running the sidecar directly
In most cases you do not need to run daprd explicitly, as the sidecar is either launched by the CLI (self-hosted mode) or by the dapr-sidecar-injector service (Kubernetes). For advanced use cases (debugging, scripted deployments, etc.) the daprd process can be launched directly.
For a detailed list of all available arguments run daprd --help or see this table which outlines how the daprd arguments relate to the CLI arguments and Kubernetes annotations.
Examples
-
Start a sidecar alongside an application by specifying its unique ID.
Note:
--app-idis a required field, and cannot contain dots.daprd --app-id myapp -
Specify the port your application is listening to
daprd --app-id --app-port 5000 -
If you are using several custom resources and want to specify the location of the resource definition files, use the
--resources-pathargument:daprd --app-id myapp --resources-path <PATH-TO-RESOURCES-FILES> -
If you’ve organized your components and other resources (for example, resiliency policies, subscriptions, or configuration) into separate folders or a shared folder, you can specify multiple resource paths:
daprd --app-id myapp --resources-path <PATH-1-TO-RESOURCES-FILES> --resources-path <PATH-2-TO-RESOURCES-FILES> -
Enable collection of Prometheus metrics while running your app
daprd --app-id myapp --enable-metrics -
Listen to IPv4 and IPv6 loopback only
daprd --app-id myapp --dapr-listen-addresses '127.0.0.1,[::1]'
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.